7 tips to protect yourself from stroke
0
The main factors that make us more vulnerable to stroke are age and heredity. Of course, you can't turn back the years or change your family history, but there are many other factors that increase the risk of stroke and you can control them. Of course, if you know about them. We found out everything about stroke.
Why do people have strokes?
Scientists have found that in 85 percent of cases, hypertension and also arterial hypertension are considered the causes of stroke in humans.
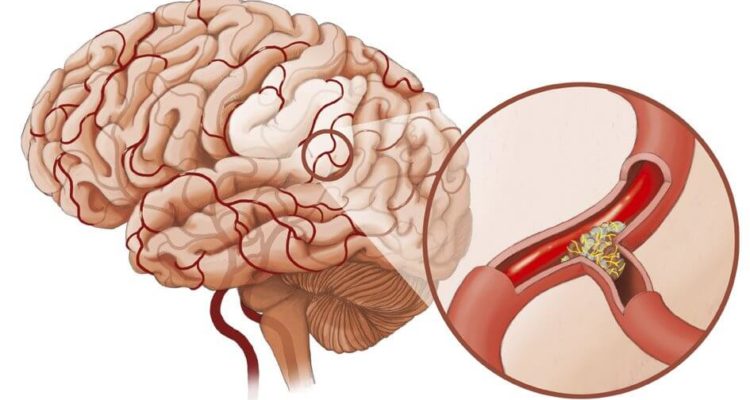
In general, this life-threatening pathology occurs due to rupture of cerebral vessels. It is after this that hemorrhage occurs in the body into the brain tissue, hematomas and clots are formed, which lead to edema and the development of the so-called stem syndrome. In addition, several processes occur simultaneously: pressure increases, aneurysms and malformations appear.
If you know that a certain factor in your health increases your risk of stroke, you can take steps to mitigate its effects. It is important to know if you have a hereditary predisposition.
7 ways have been identified that reduce the risk of stroke
1. Try to lower your blood pressure
High blood pressure is a major factor that doubles or even quadruples the risk of stroke if it is not controlled. Hypertension is considered a common factor that increases the risk of stroke, it simply needs to be controlled.
Your ideal goal: BP support, will not reach the 120/80 mark. But despite certain individual characteristics, for a certain category of people it is worth following other frameworks (for example, 140/90).
What to do: Reduce the amount of sodium in your daily diet to 1-2 g. Choose meat products with a low fat content. Make it a habit for you to eat plant-based foods, whole grain foods, and low-fat dairy products every day.
Fish should be eaten several times a week. More exercise: You need to exercise at least half an hour a day (more if possible). Quit smoking if you do. If necessary, take medication to lower blood pressure (self-medication can harm your health).
2. Get rid of excess weight.
Obesity and the complications associated with obesity increase your chances of having a stroke. Note that losing even five kilograms will significantly reduce the risk of stroke.
Your goal: Keep your body mass index (BMI) at or below 25.
What to do: Try to eat between 1,500 and 2,000 calories a day. Watch your exercise and try to stay active: walk, skip the elevator, find a sport that suits you and do it regularly.
3. Exercise, exercise, and more exercise!
Exercise not only helps you lose weight and lower your blood pressure, but it also has a positive effect on reducing your risk of stroke, regardless of these factors.
Your goal: Exercise moderately at least five days a week.
What to do: Take a walk every morning after breakfast. Join a gym with friends. When exercising, reach a level where you are breathing heavily but can still talk (this is an indicator of sufficient exercise intensity). Use the stairs instead of the elevator whenever possible. If you don’t have 30 minutes to exercise at a time, break that time into several 10- or 15-minute sessions.
4. Limit your alcohol intake
Limiting your alcohol intake can reduce your risk of stroke to a minimum. Studies show that if you drink one alcoholic drink a day, your risk may be lower. It increases significantly once you start drinking more than two drinks a day.
Your goal: Drink alcohol in moderation.
How to achieve this: Limit yourself to one glass of alcohol per day. Opt for red wine, as it contains resveratrol, which has a positive effect on the heart and brain. Watch your portion sizes. It should not exceed the standard drink size: 150 grams of wine, 0.33 liters of beer or 50 grams of hard liquor.
5. Be sure to treat atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a form of irregular heartbeat that causes blood clots. These clots can then travel to the brain, causing a stroke. Fibrillation increases your risk of stroke by almost 5 times and should be taken seriously.
Your goal: If you have been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, you need to get it treated.
What to do: If you have symptoms like a fast heartbeat or shortness of breath, make an appointment with your doctor to get tested. You may need to take blood thinners.
6. Treat your diabetes
High blood sugar damages blood vessels, making them more likely to clot.
Your goal: Don't let your blood glucose levels rise.
What to do: Use diet, exercise, and medication to keep your glucose levels within the recommended range.
7. Quit smoking
Smoking affects blood clot formation in several ways. It thickens your blood, which increases the amount of plaque that builds up in your arteries. Along with a healthy diet and exercise, quitting smoking is considered one of the most powerful factors that can help you significantly reduce your risk of stroke.
Your goal: Quit smoking. This will have a positive effect on your body.
What to do: Ask your doctor to determine the most suitable way for you to quit smoking. Use the methods he recommends: Nicotine tablets or patches, psychological counseling. Don't give up. Most smokers need several attempts to quit. Consider each attempt a step towards your goal.








Leave a Reply