Bronchitis: what to do if the cough does not go away
0
It is necessary to take antibiotics in rare cases.< /p>
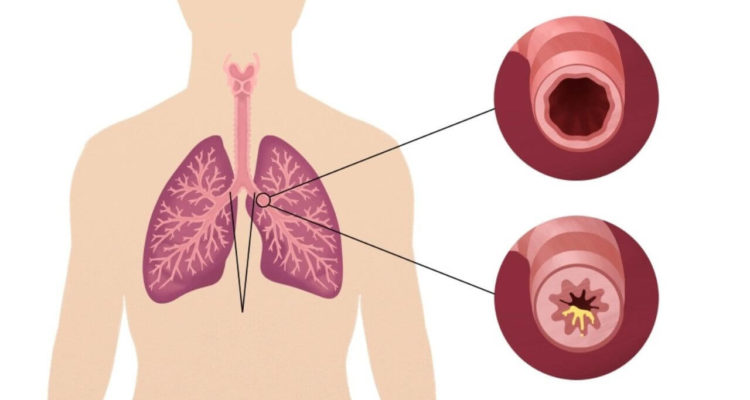
What is bronchitis and what does it look like
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi, tubes that carry air from the trachea to the lungs and back, which is accompanied by a cough.< /p>
There are two types of the disease. The first is acute bronchitis. It usually goes away within 10 days, although the cough may persist for several weeks. Sometimes, without proper treatment, inflammation can lead to pneumonia.
The second type is chronic bronchitis. This is a constant irritation and inflammation of the bronchi, which is one of the types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Where does bronchitis come from
The main cause of acute bronchitis is a viral infection. It can be transmitted from an infected person to others by coughing, sneezing, talking, or by contact.
But sometimes inflammation of the bronchi is caused by other factors:
- bacteria or fungi;
- external irritants – steam, dust, smoke, including from cigarettes;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease, when acid from the stomach causes heartburn and can enter the bronchi through the larynx.
- cough with clear or greenish sputum;
- shortness of breath;
- wheezing;
- chest tightness, difficult breathing ;
- sore throat;
- high body temperature;
- chills;
- fatigue and weakness.
- X-ray of the chest. The picture determines whether pneumonia has developed.
- Analysis of sputum. Helps to understand whether antibiotics are needed to kill the bacterial infection.
- Functional lung tests, or spirometry. A person blows into a special device that measures the volume of exhaled air and the speed of its removal. This study is necessary for the differential diagnosis of emphysema and asthma.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers – to bring down the temperature.
- Expectorants – if sputum comes out with difficulty when you cough.
- Inhalers for dilation of the bronchi.
- Antibiotics. Sometimes they are prescribed if a bacterial infection develops.
- Bronchodilators. These are inhalers that expand the lumen of the bronchi.
- Steroid hormones. They are also available as an inhaler and help reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics. They are needed if a bacterial infection develops.
- Avoid cigarette smoke. It increases the risk of developing chronic bronchitis, as it damages the respiratory tract.
- Get a flu shot. It often causes acute bronchitis.
- Wash your hands more often. This will help to avoid contracting a viral infection.
- Put on a surgical mask. For people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, it will help protect them from dust or vapors at work, and in crowds – from infection. This will reduce the number of exacerbations.
>
ul>
Chronic bronchitis occurs most often due to smoking, inhalation of dust and chemicals, and sometimes due to genetic pathology – deficiency of alpha-1-antitrypsin protein. It is needed to protect the lungs from the enzyme elastase, which is released during inflammation.
What are the symptoms of bronchitis
The following symptoms are characteristic of both the acute and chronic types :
What to do when symptoms of bronchitis appear
You should go to a therapist, and if the temperature is above 38 °C, you can call him home. The doctor will listen to the lungs, this is enough to make a diagnosis. Although in some cases the specialist prescribes an additional examination:
How is bronchitis treated
It all depends on the type of disease.
Acute bronchitis
Doctors advise to rest, drink more fluids, but without alcohol and caffeine. The air in the house should be humidified using a steam generator or another available method. You may also be prescribed medications:
But folk remedies do not help with bronchitis. Compresses, mustards, hot foot baths and jars create the illusion of care, but they are powerless against viruses and bacteria.
Chronic bronchitis
Treatment usually includes drugs and recommendations to change your lifestyle. Yes, doctors advise you to quit smoking and avoid second-hand smoke, do physical exercises to train your respiratory muscles.
There is no cure for chronic bronchitis. Medicines only help to reduce symptoms. These can be:
If a person with chronic bronchitis has a low level of oxygen in the blood, he will be prescribed oxygen therapy or inhalation of an oxygen mixture. And in severe cases, a lung transplant is performed.
How to prevent the development of bronchitis
For this, experts from the reputable medical organization Mayo Clinic advise:
Source storinka.com.ua








Leave a Reply