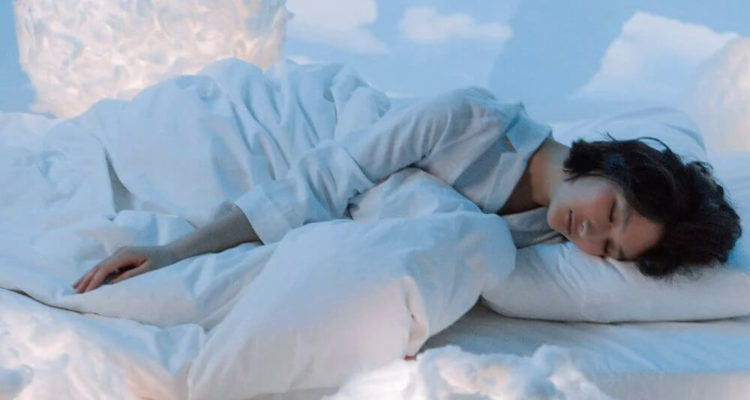

Less than five hours of sleep significantly increases the risk of dementia in old age
1
Dementia affects its patients, gradually impairing their memory and depriving them of their independence. Fortunately, preventive measures against the disease are great. The results of one study show that sleeping less than five hours each night can have serious consequences for the brain.
Sleep and dementia are a complex topic. Different types of dementia are associated with different sleep problems.
Dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease appear to be particularly associated with mild sleep disturbances, and some studies have shown that mild sleep disturbances are a very early sign of these conditions, especially in older men.
A 2021 study by the Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders examined the relationship between multiple sleep disorders and the risk of dementia.
The results showed that the risk of dementia was twice as high among people who slept less than five hours a night compared to those who slept between seven and eight hours.
Lead author of the study Rebecca Robbins from the Department of Sleep and of Circadian Disorders said the findings suggest that inadequate sleep duration may increase the risk of dementia and underscore the importance of good sleep habits.
According to the Alzheimer's Society, good sleep is linked to good health. , including with cognitive health.
“Researchers studied whether there are effective methods of treating poor sleep and whether these methods can affect the risk of developing dementia. Some medications for poor sleep, such as benzodiazepines, have been associated with an increased risk of dementia, although the evidence for the link is conflicting. Many treatments that have been proposed to improve sleep quality involve lifestyle changes. Regular sleep patterns, eating patterns and diets, exercise and providing bright light in the morning are all ways to improve sleep quality.”







Leave a Reply