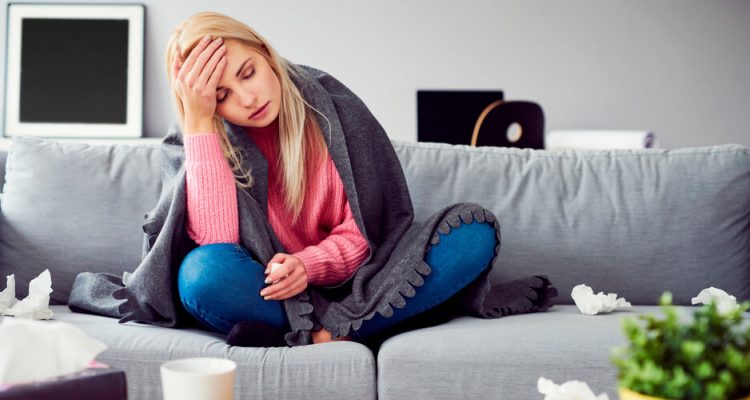

They got sick: what do you have a real flu or a cold?
0
for a fairly innocent cold and real flu is different pathogens, but symptoms are often very similar. Meanwhile, it is important for treatment to distinguish uncomplicated respiratory infections (influenza, cold) from influenza-true influenza. A sick person can secrete pathogenic microorganisms for about two to ten days, in exceptional cases, for example, in the treatment of certain medicines (steroids), even longer.
colds . Typical cold symptoms are:
- throat redness and moderate sore throat,
- chills,
- Muscle pain,
- Sweating,
- General weakness,
- Headache,
- Sore throat,
- Dry cough,
?In patients, however, there is a low fever or absence thereof, one of the differences in cold cold. Even people with respiratory diseases, such as allergic asthma, usually do not have more serious symptoms in viral colds than people without these diseases. At the same time, if asthmatics is faced with the causes of their disease, they can show more severe symptoms of the disease and be prone to asthma attacks. But often the flu is typically a very sudden onset – with a sharp deterioration of health and fever up to 39 degrees. This can also be observed:
In elderly patients, influenza often begins unnoticed. As a rule, the symptoms last from 7 to 14 days, with a general feeling of weakness and loss of appetite, which can persist for several weeks. The incidence of influenza in this group of patients is higher. in general, unlike colds, real flu can cause very serious consequences. In principle, complications may occur at any age, but they mainly apply to people with major diseases (chronic heart disease, lungs or metabolism, immunodeficiency, etc.). Influenza viruses. Children may develop an ear infection (otitis). Sick young children particularly contagious: they spread viruses longer than adults.








Leave a Reply