
This type of fatty acid reduces the risk of dementia by a whopping 60%
0
Research makes a strong case for adding one product to your weekly menu.
Food plays a variety of roles in everyday life, from satisfying cravings to keeping you fit. While eating to reduce the risk of dementia may sound too good to be true, a doctor suggests it may work. A weekly portion of certain meats can reduce the risk of brain disease by 60 percent.
Your diet can have a very powerful effect if you choose the right foods, and dementia is not immune to diet either.
< p>Consumption of “PUFA” can reduce the risk of developing the condition on a whopping 60 percent.
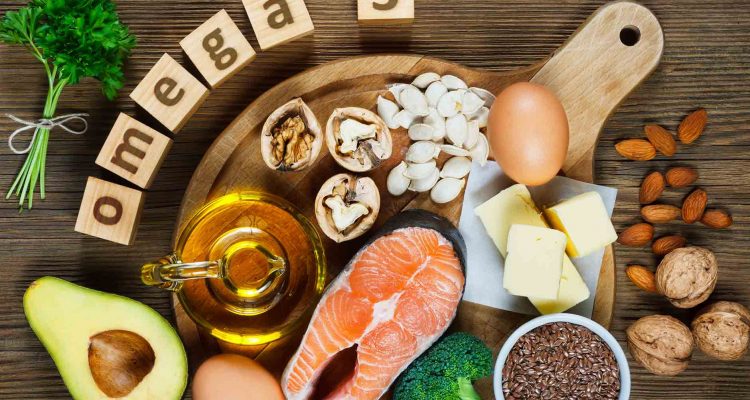
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs) that have particular benefits for brain health. There are three main types of omega-3s: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). Omega-3 fatty acids make up most of the membranes of neuronal cells in the brain and spinal cord. Membrane structure and function are critical to optimal brain function because without them, the cell cannot transmit cellular messages properly.
Once you get these fatty acids from your diet, they act as a “powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory means”. Your whole body, including your brain, can benefit from omega-3s, including a lower risk of dementia.
What's more, many people like natural food sources of omega-3s, and fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, herring, sardines, and tuna offer the highest content.
Makes a compelling case for eating fatty fish. After studying 815 participants aged 65 to 94, scientists found that those who ate oily fish once a week had a 60 percent reduction in dementia.








Leave a Reply