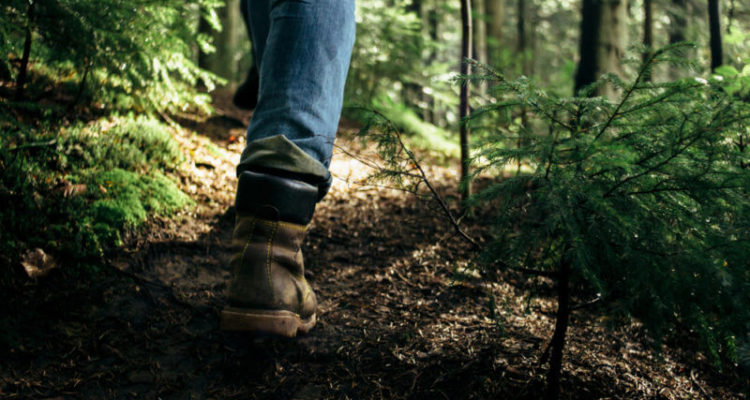

Walking can slow biological aging
0
Great news for most people who would like to stay young longer. Based on the study of the genome of more than 400,000 people, scientists from the University of Leicester have discovered a direct connection between walking speed and biological age.
British scientists have discovered a connection between walking speed and the length of telomeres – the end sections of chromosomes. which can be determined as the true biological age of a person, but also the speed of his aging. Researchers have established that if a person maintains a passion for hiking throughout his life, then already in the middle of his life he will be biologically 16 years younger than his peers who do not like to walk.
Researchers studied the genetic data of more than 400,000 middle-aged people. The faster these people walked, regardless of other types of physical activity, the longer their telomeres were. These same telomeres contain repetitive sequences of noncoding DNA that protect chromosomes from damage. Also, special caps at the end of the laces prevent them from gradually unraveling.
Each time a cell divides, the length of telomeres shortens. Until the point where they become so short that the cell can no longer go through division. Therefore, telomeres are the most powerful marker of biological age, regardless of when a person was born and how old he is according to his passport.








Leave a Reply